STAR is a model-based, personalised, risk-based dosing strategy for glycaemic control (GC) in critically unwell sufferers. STAR gives secure, efficient control to practically all sufferers, utilizing 1-Three hourly measurement and intervention intervals. However, the typical 11-12 measurements per day required could be a medical burden in lots of intensive care items.
This research goals to considerably reduce workload by extending STAR 1-Three hourly intervals to 1 to 4-, 5-, and 6-hourly intervals, and consider the affect of those longer intervals on GC security and efficacy, utilizing validated in silico digital sufferers and trials strategies.
A Standard STAR strategy was used which allowed extra hyperglycaemia over prolonged intervals, and a STAR Upper Limit Controlled strategy restricted diet to mitigate hyperglycaemia over longer intervention intervals.
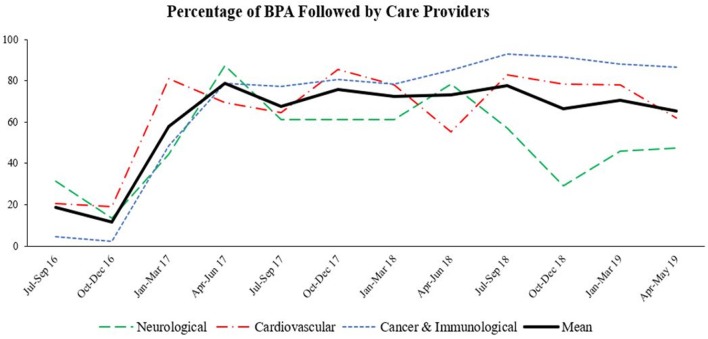
Extending STAR from 1-Three hourly to 1-6 hourly offered excessive security and efficacy for practically all sufferers in each approaches. For STAR Standard, digital trial outcomes confirmed decrease % blood glucose (BG) within the secure 4.4-8.Zero mmol/L goal band (from 83 to 80%) as therapy intervals elevated.
Longer intervals resulted in elevated dangers of hyper- (15% to 18% BG > 8.Zero mmol/L) and hypo- (2.1% to 2.8% of sufferers with min. BG < 2.2 mmol/L) glycaemia. These outcomes have been achieved with barely diminished insulin (3.2 [2.0 5.0] to 2.5 [1.5 3.0] U/h) and diet (100 [85 100] to 90 [75 100] % aim feed) charges, however most significantly, with considerably diminished workload (12 to Eight measurements per day).
The STAR Upper Limit Controlled strategy mitigated hyperglycaemia and had decrease insulin and considerably decrease diet administration charges.The modest elevated threat of hyper- and hypo-glycaemia, and the discount in diet supply related to longer therapy intervals signify a major threat and reward trade-off in GC.
However, STAR nonetheless offered extremely secure, efficient control for practically all sufferers no matter therapy intervals and strategy, displaying this distinctive risk-based dosing strategy, modulating each insulin and diet, to be strong in its design. Clinical pilot trials utilizing STAR with completely different measurement timeframes needs to be undertaken to verify these outcomes medically.
The addition of PNI to the ultimate fashions improved predictive
The prognostic dietal index (PNI), an immunity and diet based mostly prognostic rating, was correlated with medical outcomes in several tumors.
However, the prognostic significance of PNI has not been investigated in hormone delicate prostate most cancers (PCa). The goal of this research was to decide the prognostic significance of PNI in hormone delicate PCa.Two hundred eighty PCa sufferers present process androgen deprivation remedy (ADT) as first line remedy at three facilities have been enrolled.
The serum albumin ranges and peripheral lymphocyte depend have been measured on the time of prognosis. PNI was calculated as 10 * serum albumin (g/dL) + 0.005 * whole lymphocyte depend (per mm3). Patients have been categorized in two teams utilizing a cut-off level of 50.2 as calculated by the receiver-operating curve evaluation. Univariate and multivariate cox regression analyses have been carried out to consider PNI as a good prognostic issue for progression-free survival (PFS), cancer-specific survival (CSS) and general survival (OS).
Prognostic accuracy was evaluated with the Harrell concordance index.Multivariate analyses recognized PNI as an impartial prognostic indicator with respect to PFS (hazard ratio (HR) = 0.521, p = 0.001), CSS (HR = 0.421, p = 0.002) and OS (HR = 0.429, p = 0.001). Patients with elevated PNI had higher medical outcomes.
The addition of PNI to the ultimate fashions improved predictive accuracy (c-index: 0.758, 0.830 and 0.782) for PFS, CSS and OS in contrast with the clinicopathological base fashions (c-index: 0.736, 0.801 and 0.752), which included Gleason rating and incidence of metastasis.Elevated pretreatment PNI was a good prognostic indicator for PCa sufferers handled with ADT.